Smart Contracts
Beginner
Updated 11/26/2025
What is
Боксы (Boxes)?
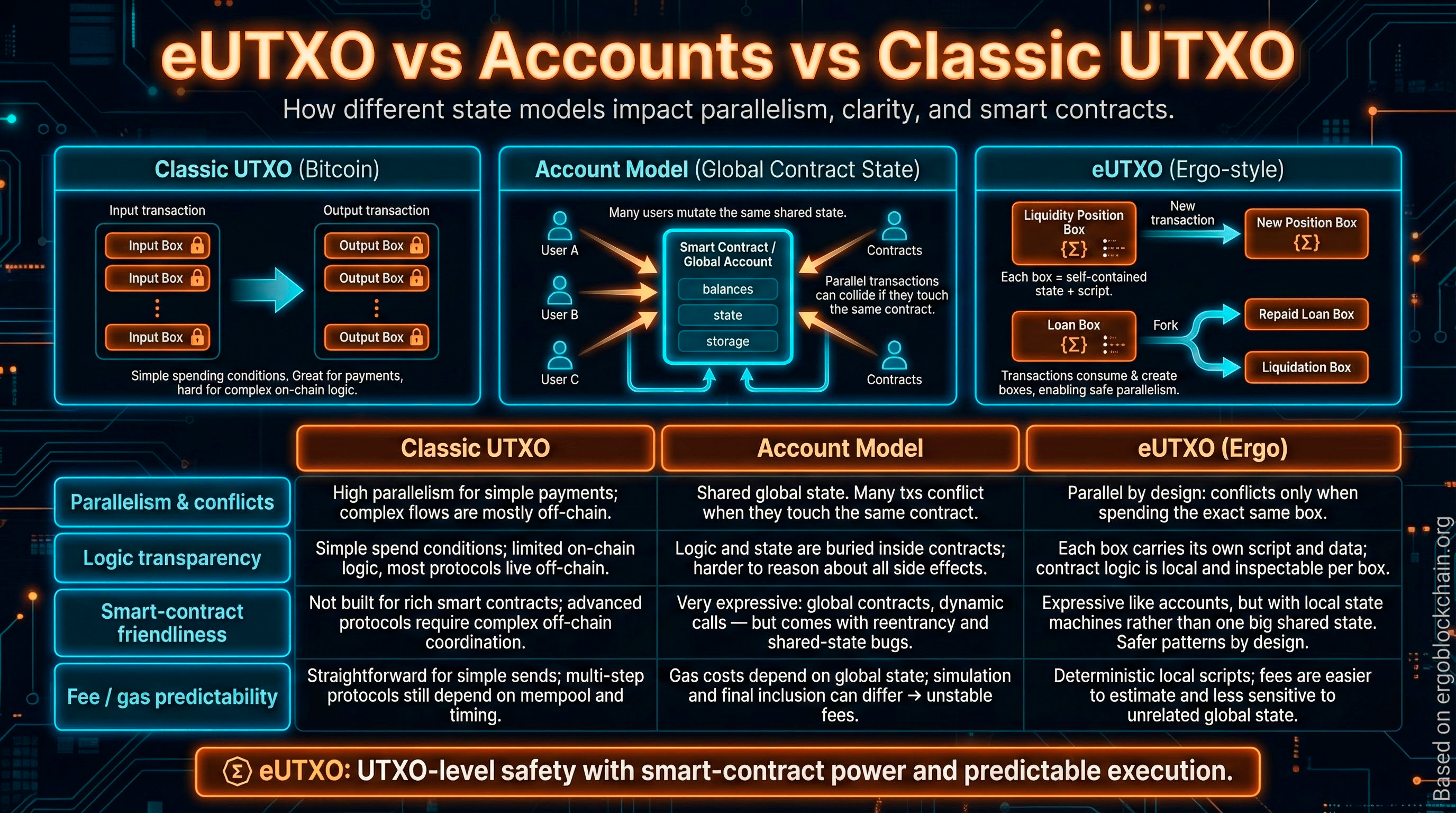
Бокс (box) — базовая «единица состояния» в eUTXO: он хранит ERG/токены, данные (регистры) и условия расходования.
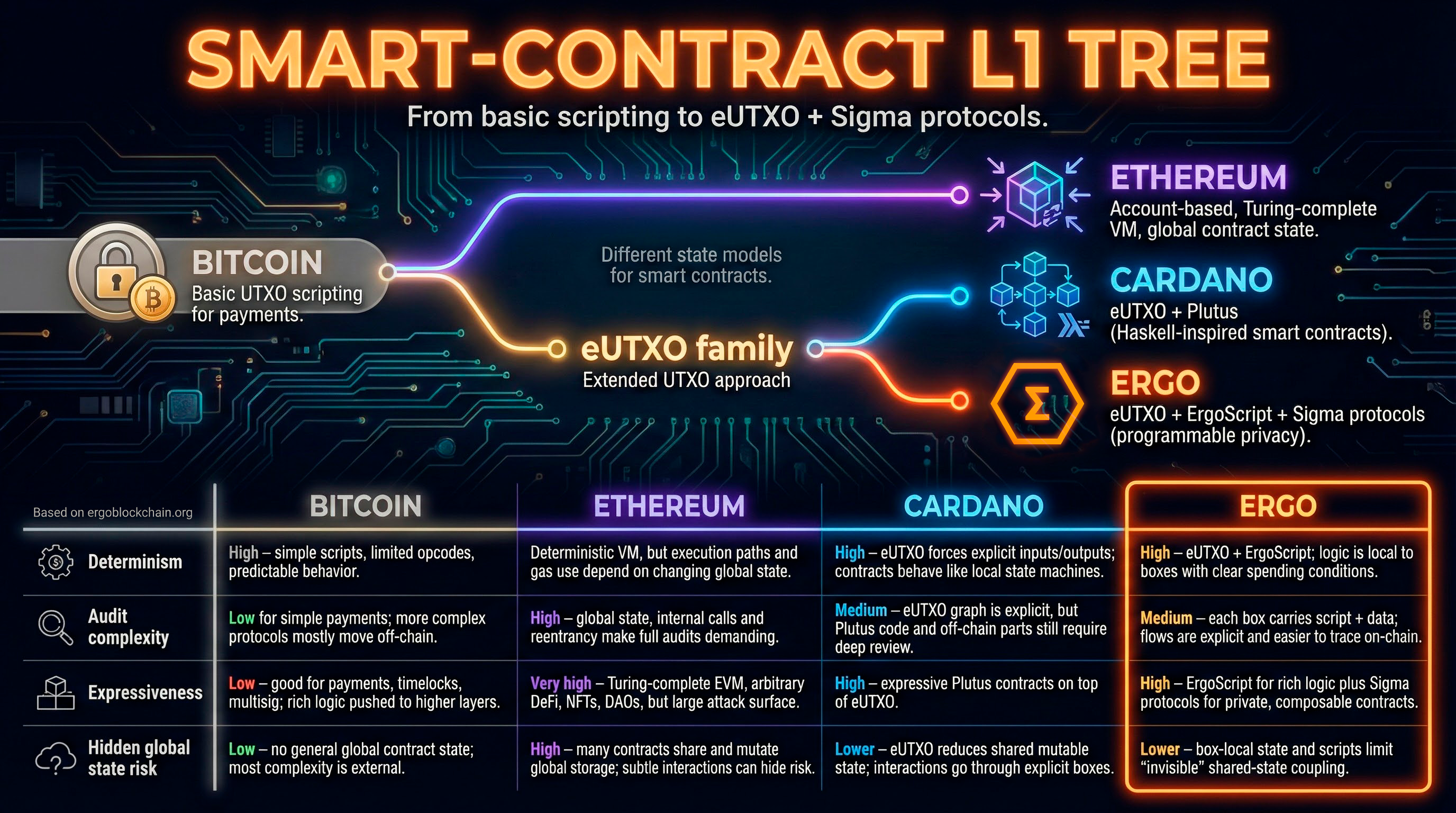
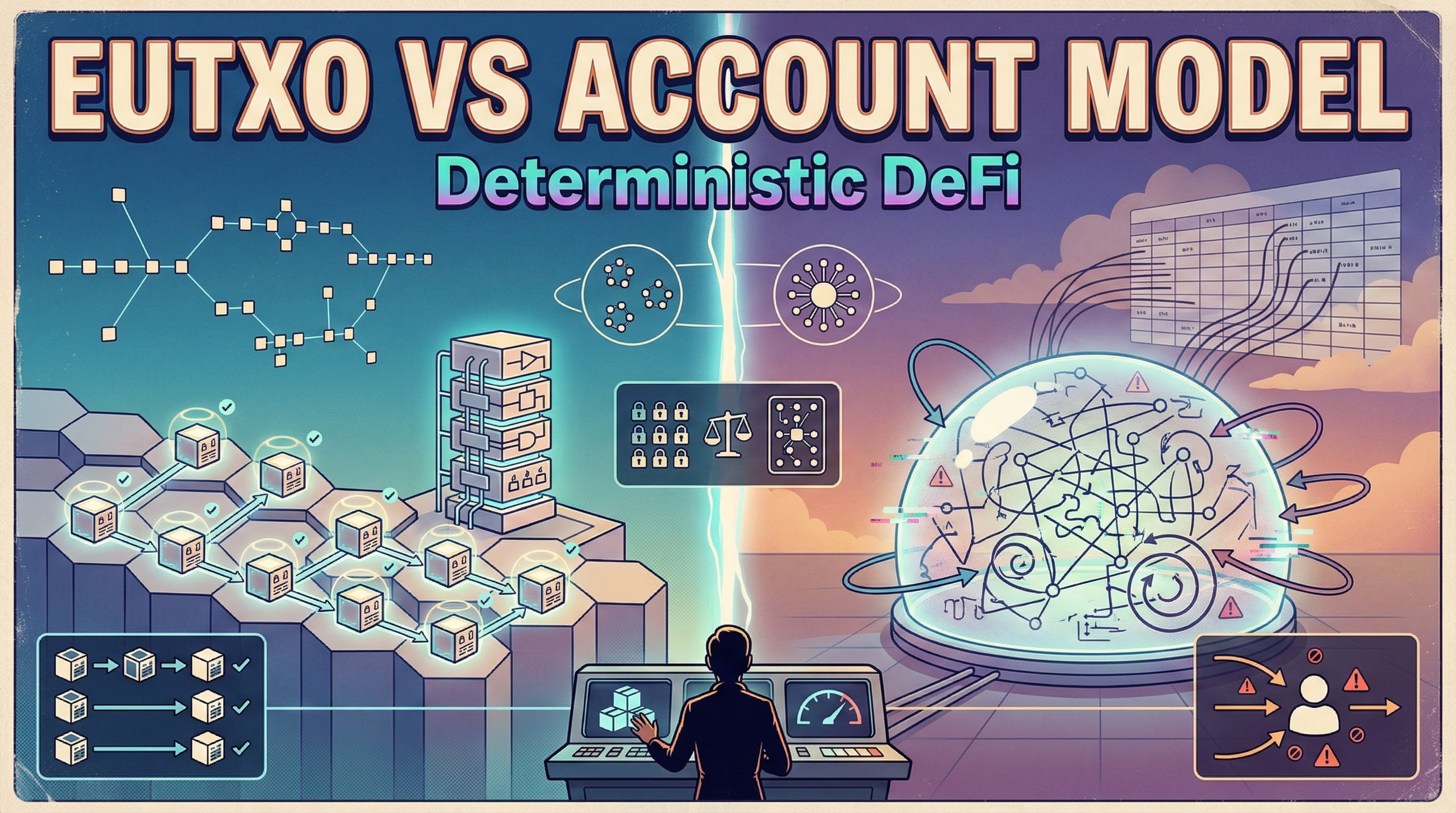
В eUTXO‑модели Ergo состояние представлено боксами. Каждый бокс содержит ценность, произвольные данные в регистрах и скрипт, который определяет правила расходования. Транзакции потребляют одни боксы и создают другие — это делает логику более детерминированной и удобной для проверки.
Key Points
- Бокс содержит ценность, данные и скрипт‑условия
- Расходование происходит через создание новой транзакции
- Регистры позволяют хранить состояние приложения прямо в боксе
- Модель поддерживает параллельную проверку независимых транзакций
Use Cases
1
DEX‑ордера и пулы ликвидности
2
NFT и токены с метаданными
3
Мультисиг и таймлок‑контракты
4
Сложные сценарии «состояния» без глобального стейта
Technical Details
Boxes are identified by a unique ID derived from the creating transaction. The minimum box value is ~0.001 ERG to prevent spam. Boxes can hold up to 255 different token types. Register data is typed (Int, Long, Coll[Byte], GroupElement, etc.) and validated by the protecting script.
Related Infographics
Related Articles
Frequently Asked Questions
Questions about Боксы (Boxes)
Common questions about this topic
Is Ergo a good investment?
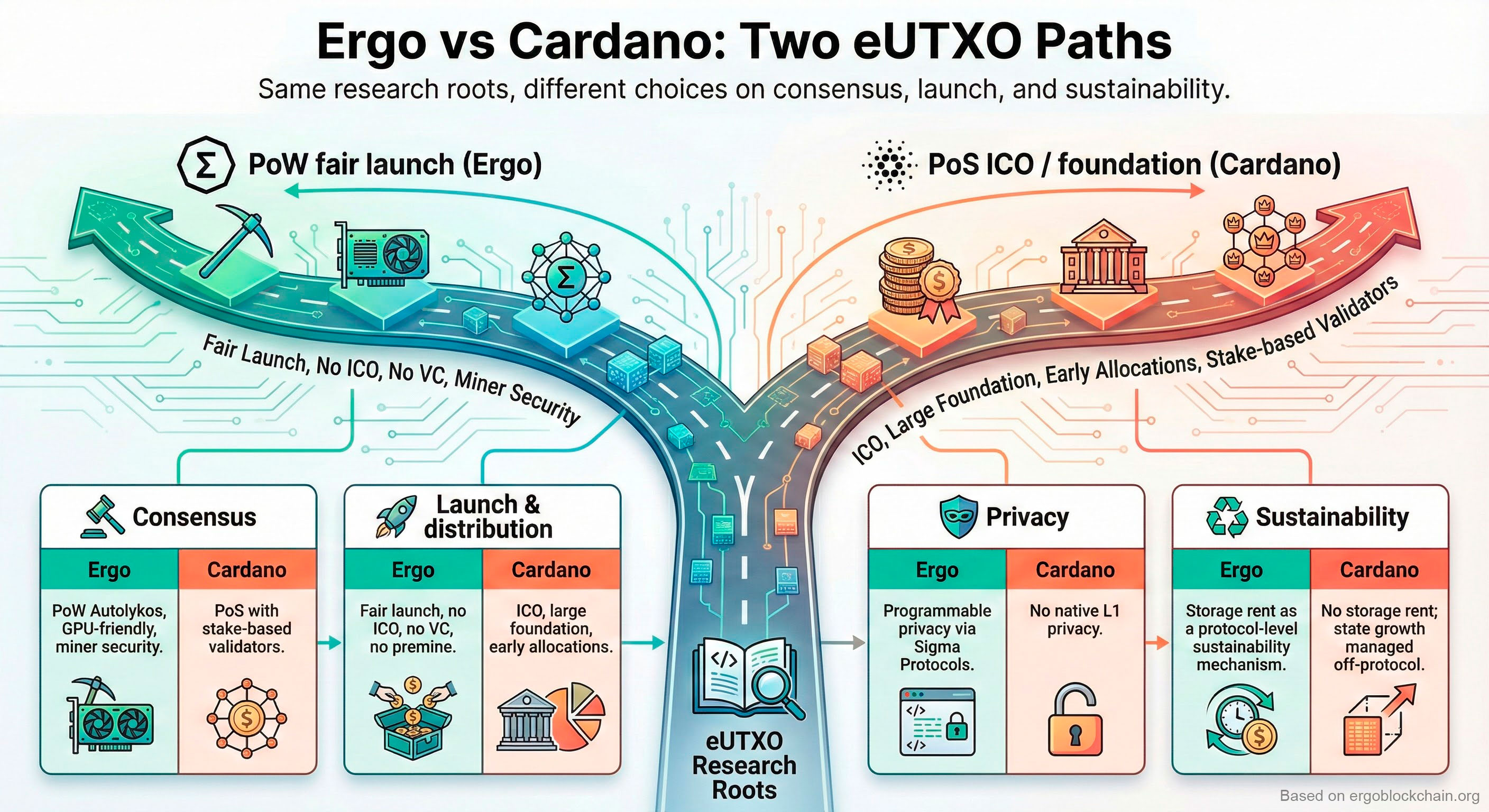
This is not financial advice. Ergo has strong fundamentals: fair launch (no VC dump risk), innovative technology (eUTXO, Sigma Protocols, NiPoPoWs), active development, and a cypherpunk ethos. It's a smaller market cap project with higher risk/reward than established chains. Research thoroughly, understand the technology, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Comparison
Getting Started
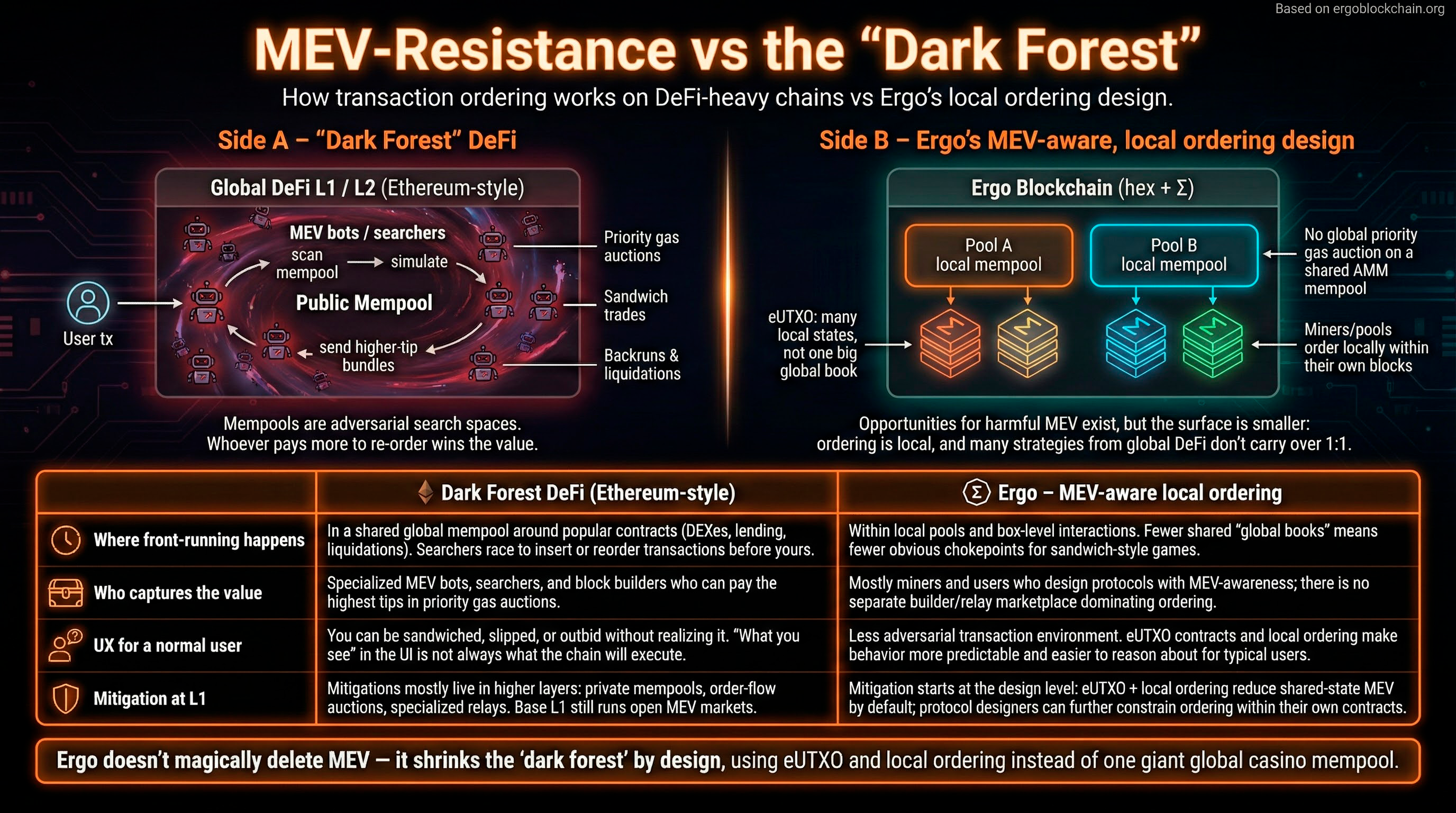
What is MEV resistance and why does Ergo have it?
MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) is profit extracted by reordering, inserting, or censoring transactions - think front-running and sandwich attacks. Ergo's eUTXO model provides structural MEV resistance: transactions reference specific boxes (UTXOs), making reordering attacks much harder. There's no shared global state to exploit like in account-based chains.
Explainer
Technology
What is storage rent on Ergo?
Storage rent is Ergo's solution to state bloat. Boxes (UTXOs) that remain unspent for 4+ years can have a small fee deducted by miners. This incentivizes cleaning up unused state, provides long-term miner revenue after emission ends, and keeps the blockchain sustainable. Lost coins eventually return to circulation instead of being locked forever.
Explainer
Technology
How to build DeFi on Ergo?
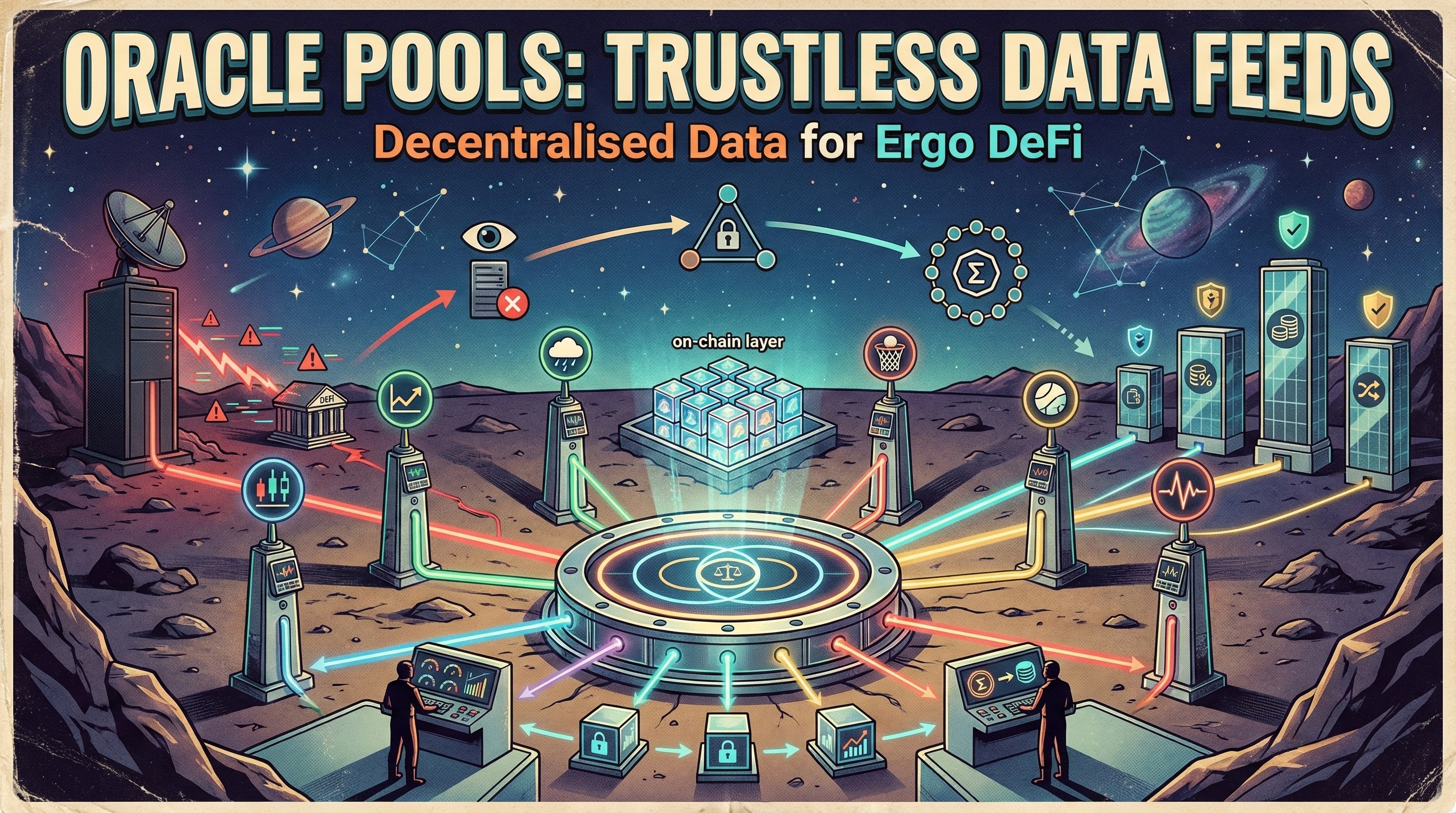
Building DeFi on Ergo starts with understanding the eUTXO model and ErgoScript. Unlike account-based chains, Ergo's box model provides deterministic execution, no MEV by design, and predictable gas costs. Use Oracle Pools for price feeds, and leverage existing patterns from Spectrum Finance and SigmaUSD.
How-to
DeFi
Related Topics
Explore More Terms
Ready to Build with Ergo Boxes?
Apply what you've learned about boxes and start building real DeFi on Ergo.